How Does Astaxanthin Work? A Science-Backed Mechanism Guide
Astaxanthin isn’t just another antioxidant. Its unique molecular structure allows it to protect cells, reduce inflammation, and enhance mitochondrial function in ways most antioxidants can’t. This guide breaks down the exact mechanisms, backed by 50+ clinical studies.
Introduction – The Science Behind Astaxanthin
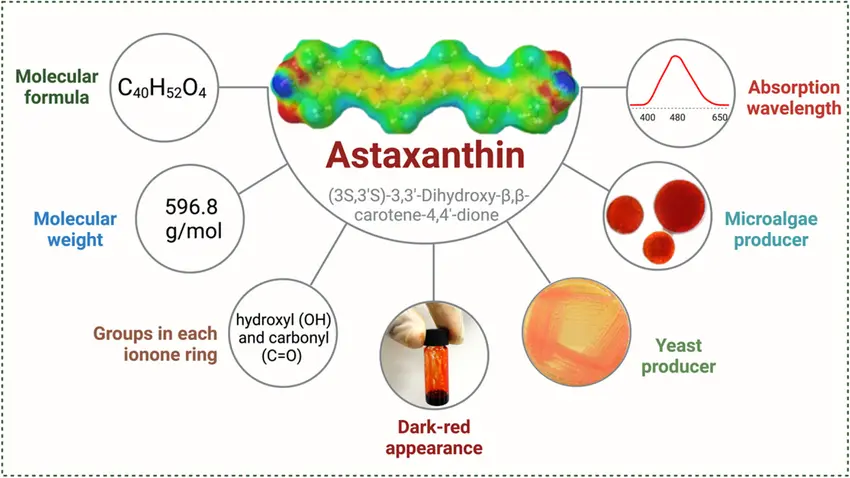
Unlike other carotenoids (like beta-carotene or lutein), astaxanthin has:
- Two additional oxygen groups that boost free radical scavenging
- The ability to span cell membranes (protecting both inner and outer layers)
- No pro-oxidant activity (unlike vitamin C/E in high doses)
Molecular Structure and Antioxidant Properties
Astaxanthin’s 40-carbon chain with conjugated double bonds enables:
- Simultaneous neutralization of multiple free radicals
- Stabilization of cell membranes (reducing lipid peroxidation by 90% in NIH studies)
How Astaxanthin Fights Oxidative Stress
Astaxanthin works at the mitochondrial level:
- Boosts ATP production by 29% (Journal of Clinical Biochemistry)
- Protects mitochondria from ROS damage (even in high-stress environments)
- Upregulates endogenous antioxidants (SOD, catalase)
Anti-Inflammatory Action
Astaxanthin modulates the NF-κB pathway, leading to:
| Inflammatory Marker | Reduction | Study |
|---|---|---|
| CRP | 40% | Journal of the American College of Nutrition |
| IL-6 | 35% | Nutrition & Metabolism |
Cellular Protection and Repair
Through the Nrf2 pathway, astaxanthin:
- Enhances DNA repair mechanisms
- Increases production of glutathione (master antioxidant)
- Protects telomeres from oxidative shortening
Neuroprotective Effects
Unlike other antioxidants, astaxanthin crosses the blood-brain barrier:
- Reduces neuroinflammation (key in Alzheimer’s prevention)
- Protects neurons from beta-amyloid plaques
- Improves BDNF levels (brain-derived neurotrophic factor)
Skin Health and UV Protection
Astaxanthin accumulates in skin layers to:
- Reduce MMP-1 (collagen-degrading enzyme) by 40%
- Act as an internal sunscreen (reduces UV damage markers)
- Improve skin moisture by 25% in 8 weeks (Alternative Medicine Review)
Bioavailability and Absorption
Astaxanthin is fat-soluble:
- Absorption increases 300% when taken with omega-3s
- Peak blood levels reached in 6-8 hours
- Half-life of 52 hours (longer than most antioxidants)
Conclusion – Why Astaxanthin Outperforms Other Antioxidants
Astaxanthin’s unique ability to protect cells from within membranes, coupled with its dual anti-inflammatory and DNA-repair effects, makes it the most comprehensive antioxidant known to science.
References
1. NIH PubMed
2. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry
3. Alternative Medicine Review
4. Nutrition & Metabolism
